Tokyo Food Safety Information Center » Tokyo Metropolitan Government food safety FAQ »I’ve heard that large amounts of anti-mold agents are used on imported lemons and grapefruits; do these have any harmful effects on the human body?
I’ve heard that large amounts of anti-mold agents are used on imported lemons and grapefruits; do these have any harmful effects on the human body?

I’ve heard that large amounts of anti-mold agents are used on imported lemons and grapefruits; do these have any harmful effects on the human body?
Are there any usage limits?
Can I check the labels and so on to see whether anti-mold agents have been used?
Does the anti-mold agent come off it I wash the fruit well?

Anti-mold agents is sometimes used on imported citrus fruit. However, usage limits have been established so that it does not impact on health.


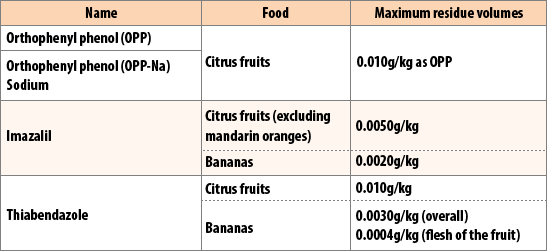
Japan’s Food Sanitation Act stipulates the standard for the anti-mold agents used on citrus fruits and bananas, including the foods that it can be used for and the maximum residue volumes. Typical usage limits for anti-mold agents are shown in the table below.
Tokyo Metropolitan Government also tests imported citrus fruits and bananas for anti-mold agent residues to check that they are safe.
In addition, there is mandatory labeling on packaging when anti-mold agents has been used. Specifically, the name of the substance used such as “Anti-mold agents (Orthophenyl phenol)” is stated together with the purpose of its application (anti-mold agent and/or antifungal agent). When sold loose in a store, the name and purpose of the substance are displayed on the name label or display stand.
The residue of anti-mold agents is mainly on the skin of the fruit, and there is data showing that about 30% - 70% of it can be removed by washing well with water. In addition, residue can also be reduced by boiling and draining the liquid when cooking fruit.